Time Patterns for Process-aware Information Systems
Time Patterns
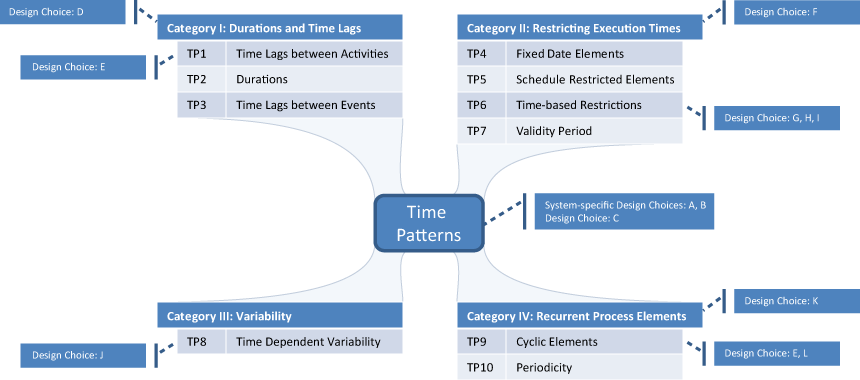
Pattern Category I: Durations and Time Lags
The first pattern category comprises three time patterns expressing durations for different kinds of process granularities (e.g., activities) as well as time lags between activities or events.
Pattern Category II: Restricting Execution Times
This category comprises four patterns for restricting the execution times of an activity or process (e.g., earliest start or latest completion time).
Pattern Category III: Variability
Depending on time aspects, in some processes different paths of the control flow may be chosen.
Pattern Category IV: Recurrent Process Elements
This category comprises patterns to express restrictions regarding cyclic activities / process fragments as well as periodicity.
Systematic Literature Review
In this section the results of a systematic literature review of the primary studies dealing with temporal constraints in the context of business process management is presented. Our search strategy identified over 10.000 papers of which 73 were identified as primary papers being relevant in the context of our research.
A short summary can be found in the next table.
| Bettini et al. | X | X | X | X | ||||||
| Combi et al. | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | |
| Eder et al. | X | X | X | X | ||||||
| Li et al. | X | X | X | |||||||
| Mans et al. | X | X | X | X | X | |||||
| Marjanovic et al. | X | X | X | |||||||
| Müller et al. | X | X | ||||||||
| Sadiq et al. | X | X | X | X | ||||||
| Zhuge et al. | X | X | X | X |
More detailed results of our systematic literature review can be found here.
Evaluations
In this section detailed evaluations of various approaches from academia and industry regarding their support of time patterns can be found.
- Calendar Systems
- Project Management Tools
- Process Modeling Notations
- Commercial Systems
- Academic Approaches