Research areas of the Professorship for Digital Business
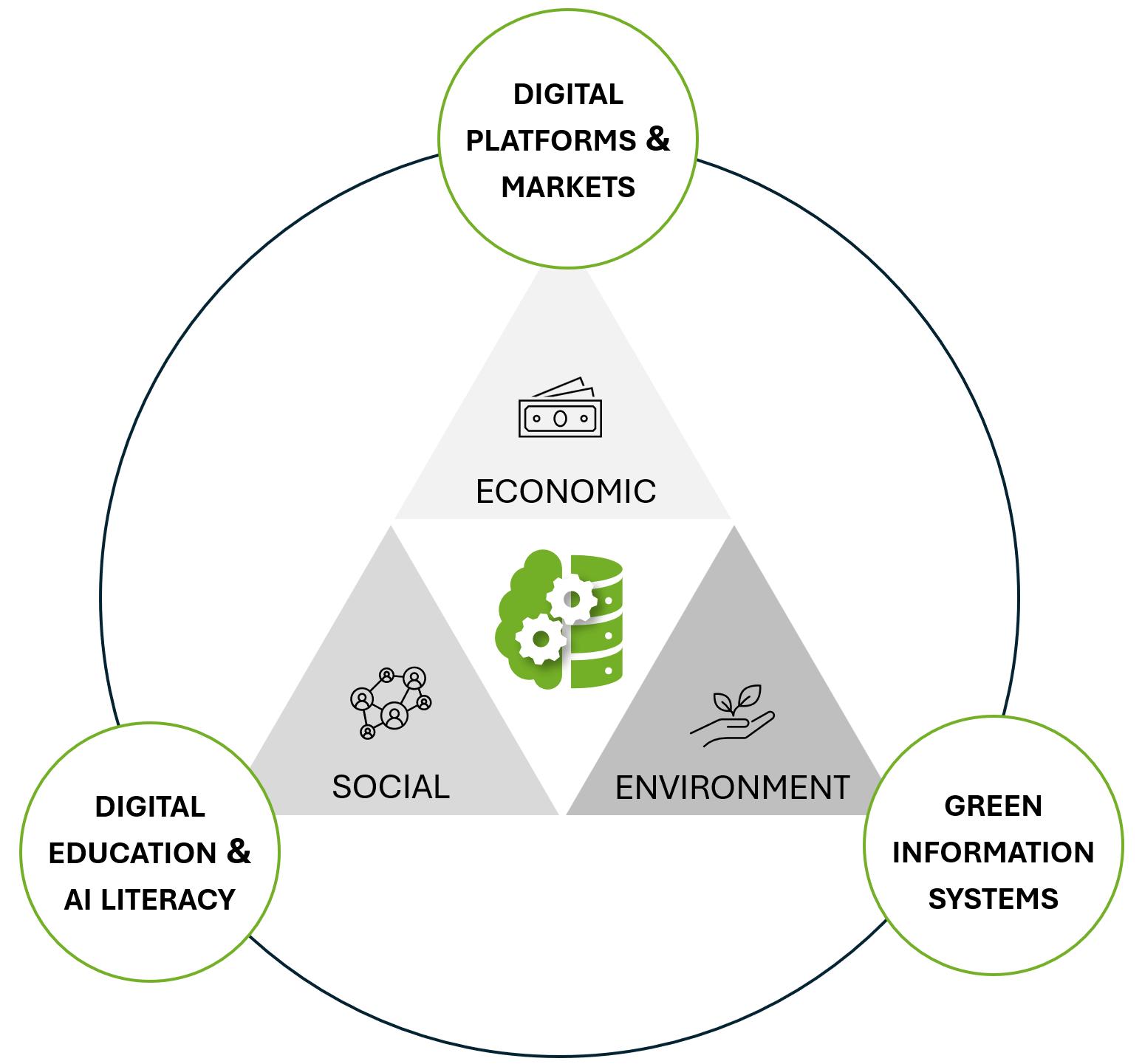
At the Professorship of Digital Business, we research and shape the future-oriented use of digital technologies to drive digital transformation in companies and society. Our aim is to go beyond the conventional economic success goals of digital transformation in the corporate context and expand the focus to sustainable value creation.
Even if the use of digital technologies may seem to contradict sustainable goals at first glance, developments such as Artificial Intelligence offer great potential for increasing efficiency, saving resources and reducing CO₂ emissions. We want to leverage this potential at the Professorship of Digital Business. In doing so, we not only support companies in their economic ambitions, but also promote the three pillars of sustainability - economic viability, social and environmental responsibility - for a positive digital transformation of the economy and society.
Our research is divided into the research areas Digital Platforms & Markets, Digital Education & AI Literacy, and Green Information Systems.
Digital Platforms & Markets
The digital transformation has led to the emergence of digital platforms that are transforming traditional one-sided markets into two- or multi-sided markets. The aim of this research area is to gain a comprehensive understanding of the underlying mechanisms of such markets. Based on these findings, new design features for digital platforms will be developed with the help of innovative technologies such as Artificial Intelligence. Their impact on market participants and social welfare will be analysed and, if necessary, proposals for necessary regulatory mechanisms will be developed.
Our research in the area Digital Platforms & Markets
Projects
EcoDeShare - Ökonomie und Gestaltung von Sharing Plattformen (FWF - Austrian Science Fund)
Selected Publications
Napirata, S.; Sedlmeir, J.; Rieger, A.; Fridgen, G.; Zimmermann, S. (2023): The Competition Effect of Decentralized Platforms: An Analytical Model. International Conference on Information Systems (ICIS) 2023. Hyderabad. Indien.
Napirata, S., Kupfer, A., Zimmermann, S., Nault, B. R. (2021): Platform-based sharing of 'need-to-use' goods. Workshop on Information Systems and Economics (WISE) 2021. Austin, Texas. USA.
Nault, B.R.; Zimmermann, S. (2019): Balancing Openness and Prioritization in a Two-Tier Internet. Information Systems Research 30/3, 711-1105.
Zimmermann, S.; Angerer, P.; Provin, D.; Nault, B.R. (2018): Pricing in C2C Sharing Platforms. Journal of the AIS 19/8, 671-678.
The digital transformation is increasingly shifting interactions and decisions to digital environments. Through the targeted design of these environments, users can be supported in their decision-making, for example through customer reviews, or protected against fraud, for example by recognizing fake reviews. At the same time, certain design elements, such as scarcity cues, can lead to users being pressured into potentially unfavorable decisions. With the help of experimental data analyses, we are investigating how various design elements influence the behavior of users.
Projects
EcoDeShare - Ökonomie und Gestaltung von Sharing Plattformen (FWF - Austrian Science Fund)
Selected Publications
Erlebach, S.; Kupfer, A.; Wrabel, A.; Zimmermann, S. (2023): Tagging the Fakes? – The Impact of Tagging Fake Reviews on Consumer Trust and Purchase Intention. European Conference on Information Systems (ECIS) 2023. Kristiansand, Norway.
Gutt, D.; Neumann, J.; Zimmermann, S.; Kundisch, D.; Cheng, J. (2019): Design of Review Systems - A Strategic Instrument to shape Online Review Behavior and Economic Outcomes. Journal of Strategic Information Systems 28/2, 104-117.
Habla, M.; Napirata, S.; Wrabel, A.; Kupfer, A.; Zimmermann, S. (2024): Never Again “The Pizza was Great!” – Developing Design Principles for Dynamic Review Templates. Internationale Tagung Wirtschaftsinformatik (WI) 2024. Würzburg, Germany.
Wrabel, A.; Kupfer, A.; Zimmermann, S. (2022): Being informed or getting the product? - How the coexistence of Scarcity Cues and Online Consumer Reviews affects Online Purchase Decisions. Business & Information Systems Engineering 64, 575-592.
Züllig, K., Erlebach, S., Kupfer, A., & Zimmermann, S. (2023): Bargain Hunting on Black Friday–Making Great Deals and Bragging About Them. Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences (HICSS) 2023. Hawaii, USA.
In digital markets, a large amount of customer data is generated throughout the entire purchasing process. Customer & Marketing Analytics deals with the evaluation of this data in order to gain valuable insights into customer behavior and derive targeted recommendations for action for companies. With the help of modern analytics methods, we research how these findings can be used to create personalized customer experiences and sustainably improve marketing efficiency. Recommender systems are a central field of research here: they analyze the previous behaviour and preferences of customers in order to suggest suitable products or services. Review-based recommender systems in particular offer great potential, as they combine high recommendation quality with transparent and trust-promoting explanations - an important factor in increasing user acceptance.
Projects
Next Generation Marketing Attribution - Praxisprojekt mit GetYourGuide (Auftragsforschung)
Review-basierte Erklärungen für Empfehlungen im E-Commerce - gefördert durch die Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG)
Selected Publications
Bohnen, E.; Erlebach, S.; Zimmermann, S. (2023): DrugExBERT for Pharmacovigilance – A Novel Approach for Detecting Drug Experiences from User-Generated Content. International Conference on Information Systems (ICIS) 2023, Hyderabad, India.
Röder, A.; Bohnen, E.; Züllig, K.; Kupfer, A.; Zimmermann, S. (2023): Dynamic Pricing on Two-Sided Platforms: Consequences on Customers’ Fairness Perceptions and Purchase Intentions. International Conference on Information Systems (ICIS) 2023, Hyderabad, India.
Züllig, K. (2024): Track Me if You Can – Adjusting for Tracking Uncertainty in Marketing Attribution Models. Conference on Information Systems and Technology (CIST) 2024, Seattle, WA, USA.
Züllig, K.; Bohnen, E.; Hühn, P.; Obermeier, A. (2023): Tell Me Why (I Want It That Way) – Effects of Explanations and Online Customer Reviews on Trust in Recommender Systems. International Conference on Information Systems (ICIS) 2023, Hyderabad, India.
Züllig, K.; Napirata, S.; Zimmermann, S. (2023): Context-Aware Marketing Attribution Based on Survival Analysis. Internationale Tagung Wirtschaftsinformatik (WI) 2023. Paderborn, Germany.

Digital Education & AI Literacy
New digital technologies open up a wide range of opportunities to acquire and impart skills - be it through online courses, tutorials or tool-supported learning. At the same time, the confident and reflective use of these technologies requires a high level of digital skills in order to make competent use of the exponentially growing range of data, information and opportunities for interaction. Artificial Intelligence in particular presents us with fundamental challenges and is changing social, economic and ethical framework conditions. In this context, AI literacy - the ability to understand, critically scrutinise and use AI technologies sensibly - is becoming increasingly important and a key skill for the future.
Our research in the area Digital Education & AI Literacy
Projects
Next Generation Digital Learning (Stiftung WiMa)
KI-Kompetenzen durch erfahrungsbasiertes und toolbasiertes Lernen aufbauen
Selected Publications
Förster, M., Pitz, K., Wrabel, A., Klier, M., Zimmermann, S. (2024): Building AI Literacy with Experiential Learning – Insights from a Field Experiment in K-12 Education. Internationale Tagung Wirtschaftsinformatik (WI) 2024. Würzburg, Germany.

Green Information Systems
Our research in the area Green Information Systems
Artificial Intelligence and analytics are key technologies for increasing efficiency and promoting environmental sustainability. They optimize processes to conserve resources and support the monitoring of sustainability goals. Green AI develops energy-efficient AI systems, while Responsible AI ensures social justice and ethical responsibility in order to unite environmental and social goals.
A striking example is the energy sector, a major emitter of greenhouse gases. The increasing demand for energy requires the expansion of renewable energies, which brings with it challenges such as fluctuations. Green AI and smart energy solutions help to manage these and integrate renewable energies efficiently. Analytics methods optimize energy generation, distribution, storage and use.
In an increasingly digitalized world, people are spending more and more time in digital environments and making decisions that have a significant impact on the environment. Digital Green Nudging involves the strategic use of design elements to encourage users in digital decision-making environments to make more environmentally conscious decisions through small impulses (so-called nudges) - without coercion or prohibitions. We use experimental data analysis to investigate the influence of various digital green nudges on user behavior.
Selected Publications
Habla, M.; Rupp, N.; Wrabel, A.; Seiter, M.; and Zimmermann, S. (2024): Effects of Digital Nudging in Multi-Stage Decisions - Experimental Evidence on Pro-Environmental Employee Behavior (2024). International Conference on Information Systems (ICIS) 2024. Bangkok, Thailand.
