Active Stents
Cardiovascular disease is a major cause of death in Europe [1]. Self-expandable implants, so-called stents, have been used in medicine for several decades to reopen narrowed blood vessels and reduce mortality from cardiovascular disease. However, this artificial device can cause e.g. in-stent restenosis due to the body's self-healing mechanism, which narrows the blood vessel again. The idea of so-called active stents is therefore to enable the long-term measurement of biomarkers, such as blood pressure. This makes it possible to determine the condition of the blood vessel with minimal effort.
This project aims to develop knowledge and methods for long-term integration of active electronics into self-expandable stents without impacting the mechanics or fluid dynamics. These active stents require integrated electronics for transcutaneous wireless power and data transmission, energy management and sensing.
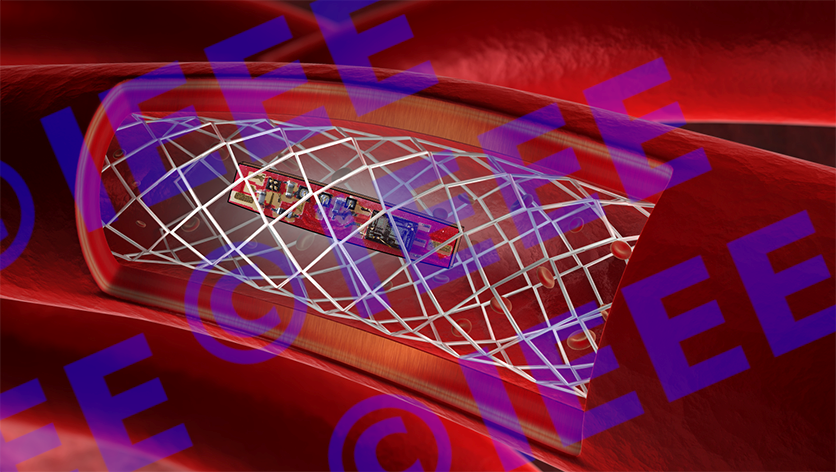
A first approach using a miniaturized PCB has already been implemented (Fig. 1). Despite the decapsulation of the majority of the components, the total size remained too large to be integrated into a blood vessel. This confirmed the necessity for an integrated solution based on an ASIC.
Publications
[1] M. Mayer; S. Reich; H. Mandry; M. Ortmanns
A Rapid-Prototyping Platform for Active Stents Utilizing Device Decapsulation for Miniaturization
31st IEEE International Conference on Electronics, Circuits and Systems (ICECS), Nov. 2024, S. 1–4
DOI: 10.1109/ICECS61496.2024.10848908
DFG Project "Active Stents" - OR245/20-1
